Throughout our lives, we see various tests designed to assess knowledge, skills, and behavior. Among these, psychological tests hold a important role in understanding human attributes, behavior, and mental functioning. Psychological testing provides a standardized approach to evaluating individual differences across diverse domains.
What is Psychological Testing?
Psychological testing is a structured, standardized procedure for measuring a sample of behavior. This process involves assessing a person’s abilities, aptitudes, or personality traits using validated instruments. The American Psychological Association (APA) defines psychological tests as standardized tools designed to measure behavior, mental attributes, and cognitive functioning, including reasoning, memory, emotional functioning, personality, and interests.
Defining Psychological Tests
- Anastasi (1982) defined a psychological test as an essentially an objective and standardized measure of a sample behavior.
- Gregory (2015) defined psychological testing is as a standardized procedure for sampling behavior and describing it with categories or scores.
- Kaplan (2005) defined a psychological test as a set of items designed to measure characteristics of human beings that pertain to behavior, whether observable (overt) or hidden (covert).
Psychological tests often aim to quantify abstract human attributes such as intelligence, emotional stability, or leadership potential. For instance- an emotional intelligence test might assess a manager’s ability to resolve conflicts effectively.
History of Psychological Testing
Psychological testing has a rich history that spans centuries, evolving from early philosophical inquiries into human nature to modern scientific methods of measurement. This journey reflects a gradual shift from subjective observations to objective, standardized tools.
1. Ancient Foundations
- Chinese Civil Service Exams- as early as 206 BCE, during the Han Dynasty, the Chinese developed structured tests to select candidates for government roles. These tests assessed knowledge, skills, and personal qualities, marking the first recorded use of standardized testing. Multiple components, akin to modern test batteries, were employed to evaluate various attributes.
- Greek Philosophers- ancient Greek philosophers like Plato and Aristotle pondered human abilities and the nature of intelligence. They explored the concept of individual differences, particularly in education and moral reasoning. While not formal tests, their writings laid the foundation for later scientific exploration.
2. The 19th Century and Scientific Beginnings
- Phrenology and Physiognomy- early attempts to understand behavior involved examining physical traits like skull shape (phrenology) or facial features (physiognomy). Though ultimately discredited, these practices highlighted the desire to link observable traits with personality and intelligence.
- Francis Galton’s Contributions- Galton, a pioneer in psychometrics, introduced objective measures to study individual differences. In 1884, he established the Anthropometric Laboratory, where visitors could measure physical traits like reaction time and sensory abilities. He introduced statistical tools like the correlation coefficient, co-developed with Karl Pearson, to analyze data. Galton’s emphasis on measurement and his concept of psychometrics laid the groundwork for modern psychological testing.
- Wilhelm Wundt and Experimental Psychology- Wundt founded the first psychological laboratory in 1879 at the University of Leipzig. He emphasized experimental methods to study mental processes, setting the stage for objective psychological measurement. Wundt’s work inspired others to develop tools for measuring mental functions.
Read More- History of Psychology
3. The Birth of Intelligence Testing
- James McKeen Cattell and Mental Tests- in the late 1800s, Cattell coined the term “mental test” to describe tools for measuring sensory and motor abilities. Inspired by Galton, Cattell developed tests to assess reaction time, memory, and other basic cognitive functions.
- Alfred Binet and the Binet-Simon Scale- in 1905, Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon developed the first intelligence test to identify children needing special education in France. The Binet-Simon Scale focused on practical problem-solving skills rather than sensory or motor abilities. Binet introduced the concept of “mental age,” a precursor to the modern IQ score. This test marked a significant departure from earlier methods by focusing on cognitive rather than physical traits.
- Lewis Terman and the Stanford-Binet Test- in 1916, Terman revised Binet’s test for use in the United States, creating the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale. He introduced the Intelligence Quotient (IQ), calculated as (mental age/chronological age) × 100. The Stanford-Binet test became a benchmark for measuring intelligence.
4. Early 20th Century
- Army Alpha and Beta Tests- during World War I, psychologists developed group intelligence tests to assess military recruits. The Army Alpha test measured verbal and numerical abilities, while the Army Beta test was designed for non-English speakers or those with limited literacy. These tests demonstrated the feasibility of large-scale psychological assessments.

Sample Items From Army Alpha Test
- Emergence of Personality Testing- the 1920s and 1930s saw the development of personality tests like the Rorschach Inkblot Test and the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT). These projective tests aimed to uncover unconscious motives and emotions. The Woodworth Personal Data Sheet, developed during World War I, was one of the first self-report personality inventories.
- Standardization and Norms- the need for reliable and valid tests led to the development of standardized procedures and normative data. Tests like the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS), introduced in 1939 by David Wechsler, provided comprehensive measures of intelligence.
5. Post-World War II Era
- Psychometric Theories- Charles Spearman developed the concept of general intelligence (g) and factor analysis to study the structure of intelligence. L.L. Thurstone challenged Spearman with his theory of multiple primary mental abilities, further refining intelligence testing.
- Aptitude Testing- Tests like the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) became widely used in educational settings to predict academic success. Vocational aptitude tests, such as the General Aptitude Test Battery (GATB), helped match individuals to suitable careers.
- Clinical Applications- The rise of clinical psychology led to the development of tests for diagnosing mental health disorders. The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI), introduced in 1943, became a cornerstone of psychological assessment.
6. Late 20th Century to Present
- Computer-Based Testing- the advent of computers revolutionized psychological testing, enabling adaptive tests that adjust difficulty based on the test-taker’s responses. Tools like the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) adopted computer-based formats for efficiency and precision.
- Cross-Cultural Testing- awareness of cultural bias led to efforts to develop tests that are fair and valid across diverse populations. The Raven’s Progressive Matrices, designed to minimize cultural influences, became widely used for cross-cultural intelligence assessments.
- Focus on Emotional Intelligence- in the late 20th century, researchers like Daniel Goleman popularized the concept of emotional intelligence, leading to tests that measure emotional and social competencies. Instruments like the Emotional Competence Inventory (ECI) became valuable in workplace settings.
- Neuropsychological Testing- advances in neuroscience spurred the development of tests to assess brain function, such as the Halstead-Reitan Battery. These tools are vital for diagnosing and managing neurological conditions like traumatic brain injuries and dementia.
- Digital and AI-Driven Assessments- recent innovations include AI-driven platforms that analyze complex patterns in responses, offering deeper insights. Mobile apps and online tests have made psychological assessments more accessible, though they raise concerns about validity and security.
Read More- Intelligence
Characteristics of Psychological Tests
Psychological tests are structured tools designed to assess various aspects of human behavior, cognitive abilities, and personality traits. To ensure their utility and credibility, high-quality psychological tests adhere to a set of key characteristics. These features enhance their reliability, validity, and applicability in diverse contexts. They include-
- Standardization- it refers to the uniformity in the administration, scoring, and interpretation of a psychological test across different settings and populations. The goal of standardization is to eliminate variability in test conditions that might influence test results. This ensures that the test produces consistent results regardless of where, when, or by whom it is administered. For example- in administering the Wechsler Intelligence Scale, all participants are given the same set of instructions, and their responses are scored using a standardized key.
- Objectivity- this ensures that the test results are free from subjective interpretation or bias from the test administrator or scorer. This characteristic ensures that personal beliefs, opinions, or biases do not influence the interpretation of test scores. For example- the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) uses a computerized scoring system to ensure that results are entirely objective and free from examiner influence.
- Behaviour Sampling- psychological tests measure a representative sample of behaviors or attributes relevant to the construct being assessed. Since it is impractical to observe all behaviors or attributes of an individual, tests are designed to sample behaviors that are indicative of broader traits or abilities. For example- an intelligence test might include tasks measuring logical reasoning, verbal comprehension, and spatial visualization to provide a comprehensive assessment of intellectual ability.
- Norms- it refer to the standardized data collected from a large, representative sample, which serves as a reference point for interpreting individual test scores. orms provide a framework for comparing an individual’s performance to that of a relevant population, helping to contextualize scores. For example- if a child scores in the 90th percentile on a standardized achievement test, this indicates that their performance is better than 90% of the normative sample.
- Reliability and Validity- reliability refers to the consistency of a test in measuring what it is intended to measure whereas validity ensures that the test accurately measures the construct it claims to measure. For example- a reliable and valid test of depression will accuratly measure depression and not another mental illness.
- Predicitions- psychological tests are often designed to predict behaviors or outcomes beyond the testing context, such as academic performance, job success, or mental health outcomes. Predictive accuracy enables the test to provide actionable insights about future behavior or performance in specific situations. For example- the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) is designed to predict a student’s potential success in graduate school.
Read More- Reliability
Classifications of Psychological Tests
Psychological tests can be classified into three main categories based of the content they measure into-
Types of Tests
- Aptitude and Achievement Tests– Aptitude tests assess an individual’s ability to learn or perform specific tasks. They are often predictive, estimating how well someone might perform in a particular job or educational setting. Whereas achievement tests, in contrast, focus on measuring the extent of an individual’s knowledge or proficiency in a specific area. They assess what a person has learned or achieved in a defined domain. For example- SAT or DBDA.
- Intelligence Tests- they measure cognitive abilities, including reasoning, problem-solving, abstract thinking, and memory. These tests aim to evaluate the intellectual potential of an individual. For example- WAIS or Raven’s Progressive Matrices.
- Personality Tests- they assess individual traits, behaviors, and emotional patterns. Unlike aptitude or intelligence tests, these tests focus on understanding personality dynamics rather than cognitive or academic skills. They can be projective or objective personality tests. For example- NEO-FFI or EPQ.
Psychological tests can be classified based on their method of administration into-
- Group Tests- they are designed to be administered to multiple individuals simultaneously, making them efficient and time-saving for large-scale assessments. For example- army alpha test.
- Individual Tests- Individual tests are administered one-on-one, allowing for a deeper exploration of the test-taker’s abilities, personality, or behavior. For example- WAIS.
Psychological tests can be classified on the basis of response format into-
- Verbal Tests- they rely on language-based tasks such as reading, writing, speaking, or comprehension to assess abilities.They uses words or language as the medium of questions and responses.They may be biased against individuals with limited language proficiency or literacy.
- Non-Verbal Tests- they assess abilities without relying heavily on language, focusing instead on visual or symbolic stimuli. It uses pictures, symbols, or shapes as stimuli. For example- SPM.

SPM
- Performance Tests- they require participants to perform tasks or manipulate objects, emphasizing practical or motor skills rather than verbal or written responses. It involves hands-on tasks like solving puzzles, assembling objects, or performing physical tasks. For example- Koh’s Block Design.
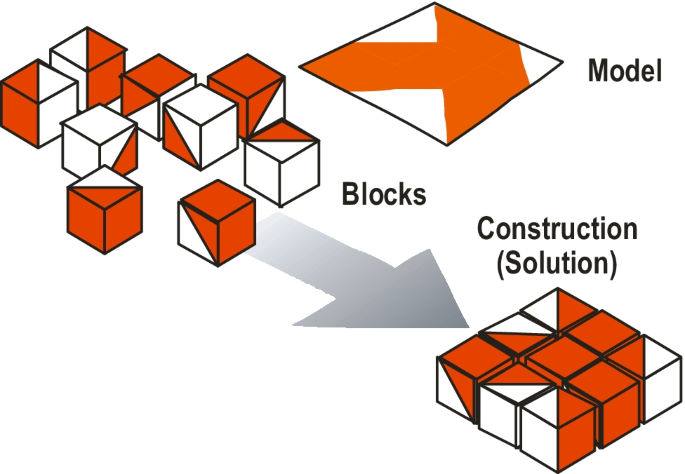
Koh’s Block Design
Read More- Validity
Uses of Psychological Tests
Psychological tests are versatile tools utilized across diverse domains to measure a wide range of attributes, including cognitive abilities, emotional functioning, and behavioral patterns. Their utility stems from their ability to provide standardized, objective, and quantifiable data about individuals or groups. Here are a few uses of tests-
- Educational Settings- they can be used to identify learning disabilities and giftedness as well as guide curriculum development and individualized instruction. For example- tests like the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) or the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale are used to identify students with learning disabilities or intellectual giftedness.
- Career and Academic Counseling- interest inventories and aptitude tests, such as the Strong Interest Inventory or the Career Assessment Inventory, guide students in choosing academic and career paths aligned with their strengths and preferences.
- Clinical Settings- tests are indispensable for diagnosing mental health issues, tracking treatment progress, and assessing cognitive functioning. For example tests like the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) or the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) assist clinicians in diagnosing mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, or personality disorders.
- Occupational Settings- organizations leverage psychological tests to optimize their workforce by assessing employees’ skills, personality traits, and potential. For example- aptitude tests, such as the General Aptitude Test Battery (GATB), evaluate candidates’ suitability for specific roles.
- Research- in psychology and related disciplines, psychological tests are vital for exploring human behavior and validating theories. For example- tests like the Raven’s Progressive Matrices (intelligence) or the NEO Personality Inventory (personality traits) provide empirical data for studying psychological constructs.
Limitations of Psychological Testing
Despite their numerous benefits, psychological tests face certain challenges that limit their efficacy and application. These limitations must be considered to ensure ethical and accurate use of tests. They include-
- Cultural and Language Bias- psychological tests are often developed within specific cultural contexts, which may not be universally applicable. Language differences and cultural norms can affect the interpretation of test items.
- Validity and Reliability Issues- a test must reliably measure the intended trait (reliability) and accurately capture the construct of interest (validity). Poorly constructed tests may fail on both counts.
- Ethical Concerns- the misuse of psychological tests can raise ethical issues, such as violations of privacy or the stigmatization of individuals. Test administrators must follow ethical guidelines, such as those outlined by the American Psychological Association (APA), and ensure informed consent and confidentiality.
- Overreliance on Scores- quantitative scores provide valuable insights but may not capture qualitative aspects of an individual’s behavior, experiences, or situational factors. For example- an intelligence test score may overlook creativity or emotional intelligence, leading to an incomplete evaluation.
- Interpretation Challenges- test results require expertise for accurate interpretation. Misinterpretation by untrained individuals can lead to incorrect conclusions or inappropriate actions.

Example of Informed Consent
Read More- Ethics in Psychological Testing
Conclusion
Psychological testing is a vital tool for assessing human behavior and attributes, with applications in education, clinical practice, organizations, and research. By categorizing tests into aptitude/achievement, intelligence, and personality tests, we gain a structured understanding of their purposes and methodologies.
Despite their widespread use, psychological tests require careful administration, cultural sensitivity, and ethical oversight to ensure valid and reliable results. As psychological testing continues to evolve, integrating advances in technology and cultural competence, its utility and impact will undoubtedly expand, offering deeper insights into human potential and behavior.
References
Anastasi, A. & Urbina, S. (2009). Psychological Testing. Pearson Education.
Gregory, R. J. (2015). Psychological Testing: History, Principles, and Applications. Pearson.
Kaplan, R. M., & Saccuzzo, D. P. (2005). Psychological Testing: Principles, Applications, and Issues. Cengage Learning India Pvt Ltd.
Singh, A. K. (2011). Tests, Measurements, and Research Methods in Behavioural Sciences (5th ed.). Bharati Bhawan.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 18,513 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2022, December 4). What is Psychological Test and Its 6 Important Characteristics. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/what-is-psychological-test/
