Introduction
Health is a multidimensional concept influenced by a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. The biopsychosocial model, introduced by George Engel (1977), offers a holistic perspective on health by integrating these three domains.
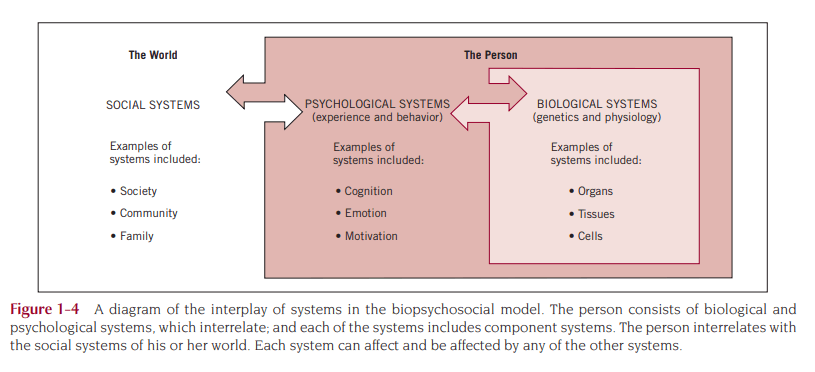
Biopsychosocial Model
This model recognizes that an individual’s health status is shaped not only by biological processes but also by psychological factors (such as cognition, emotions, and behavior) and socio-cultural influences (such as societal norms, economic conditions, and cultural beliefs). Influence of 3 important factors on health, these include gender, lifespan development, and socio-cultural factors.
Read More- Scope of Health Psychology
1. Gender and Health
Gender is an important factor that influences health, some of the ways include-
1. Biological Differences in Health by Gender
Gender, as a complex interplay of biological sex and socially constructed roles, has significant implications for health outcomes.
- Hormonal Influences- Women and men have different hormonal compositions that affect their risk profiles for various diseases. Estrogen, for instance, provides cardiovascular protection in premenopausal women, reducing their risk of heart disease compared to men. However, postmenopause, this protective effect diminishes, making women more vulnerable to heart disease (Regitz-Zagrosek, 2012).
- Genetic Predisposition- Some genetic disorders, such as hemophilia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, are more prevalent in men due to their inheritance patterns linked to the X chromosome. Conversely, women are at higher risk for autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis due to their stronger immune response.
- Pain Perception and Chronic Illness- Studies suggest that women report higher levels of chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and migraines. Biological mechanisms, including differences in nerve sensitivity and hormonal fluctuations, contribute to these variations (Fillingim et al., 2009).
2. Gendered Health Behaviors and Risk Factors
Apart from biological aspects, gender norms and socialization influence health behaviors and risks.
- Risk-Taking Behaviors- Men are more likely to engage in high-risk behaviors, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and reckless driving, which contribute to higher mortality rates (Courtenay, 2000).
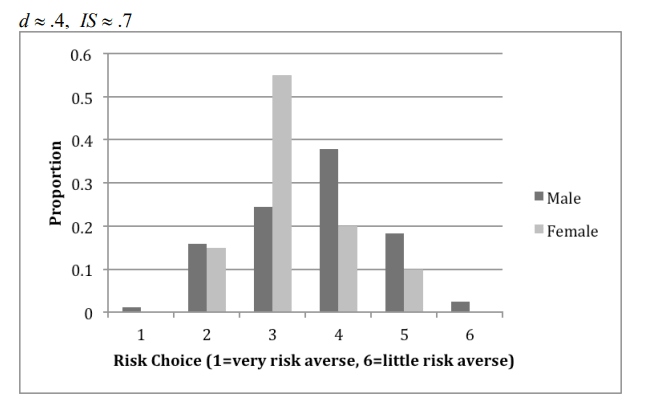
Risk Taking Behaviour Across Genders
- Healthcare Utilization- Women are generally more proactive in seeking healthcare services, including preventive screenings (mammograms, pap smears), whereas men tend to delay medical visits, often leading to late diagnoses of conditions such as prostate cancer and hypertension (Harris et al., 2009).
- Mental Health- Women are more likely to be diagnosed with anxiety and depression, whereas men are more prone to substance abuse and completed suicides. Social expectations that discourage men from expressing emotions contribute to underreporting and undertreatment of mental health disorders in men (Mahalik et al., 2003).
3. Gender Disparities in Healthcare Access and Treatment
Healthcare systems often exhibit gender biases, affecting diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes.
- Underdiagnosis in Women- Women are less likely to be diagnosed with cardiovascular diseases because their symptoms often present differently than men’s (Mosca et al., 2011).
- Pain Management Disparities- Research shows that women’s pain is often underestimated by healthcare providers, leading to inadequate pain management compared to men (Hoffmann & Tarzian, 2001).
- Cultural and Economic Barriers- In certain societies, women have less autonomy over their healthcare decisions, limiting their access to medical resources and professional treatment (Sen & Östlin, 2008).
2. Lifespan Development and Health
Health needs and risks vary across different stages of life, influenced by biological aging, psychological development, and social transitions.
1. Childhood and Adolescence
Early life experiences play a critical role in shaping long-term health outcomes.
- Nutrition and Growth- Childhood malnutrition can have lasting consequences on physical and cognitive development. Socioeconomic disparities contribute to variations in childhood health, with lower-income families experiencing higher rates of obesity and undernutrition (Story et al., 2008).
- Behavioral Foundations- Early exposure to health-promoting behaviors, such as regular physical activity and balanced nutrition, establishes habits that persist into adulthood.
- Adolescent Risk Behaviors- Adolescence is marked by increased autonomy and risk-taking, including experimentation with substance use, unsafe sexual practices, and poor dietary habits. Peer influence plays a significant role in shaping these behaviors (La Greca & Stone, 1985).
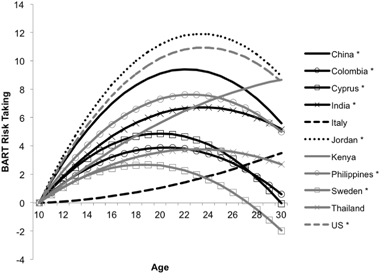
Age Patterns in Risk Taking Across the World
2. Adulthood
During adulthood, lifestyle choices significantly impact long-term health.
- Workplace Stress and Health- Occupational stress contributes to mental health issues, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases (Diehr et al., 1993).
- Reproductive Health- Women’s reproductive years involve unique health concerns, including pregnancy-related risks, contraception, and menopause.
- Chronic Disease Onset- Middle age is often when chronic illnesses such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and obesity manifest, influenced by lifestyle factors and genetic predispositions (USBC, 2010).
3. Aging and Late Adulthood
Aging presents physical, cognitive, and social challenges that impact health.
- Cognitive Decline and Dementia- Aging increases the risk of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, with women being disproportionately affected due to longer life expectancy (Cattan et al., 2005).
- Social Isolation and Mental Health- Older adults often experience loneliness and depression, particularly those without strong family or community support (Hayman, 2007).
- Healthcare Accessibility- Mobility issues, financial constraints, and inadequate social support systems pose barriers to accessing healthcare services in old age.

Seeking Treatment Based on Sex, Wealth, and Urbanicity
3. Socio-Cultural Factors in Health
Health is deeply influenced by cultural norms, economic conditions, and social environments.
1. Socioeconomic Status (SES) and Health Disparities
- Income and Healthcare Access- Lower SES is associated with poorer health outcomes due to limited access to healthcare, nutritious food, and safe living environments (Marmot, 2005).
- Education and Health Literacy- Higher educational attainment correlates with better health knowledge and decision-making, leading to healthier behaviors and increased healthcare utilization.
- Occupational Hazards- Low-income workers often have higher exposure to workplace hazards and job-related stressors, increasing their risk for occupational diseases.
2. Cultural Beliefs and Health Practices
- Traditional vs. Modern Medicine- Many cultures integrate traditional healing practices alongside modern medicine, which can influence healthcare-seeking behaviors.
- Stigma and Mental Health- Cultural attitudes toward mental health vary widely; in some societies, mental illness is heavily stigmatized, discouraging individuals from seeking professional help (Kleinman, 1980).
- Gendered Expectations- Cultural norms around masculinity and femininity shape attitudes toward health, with some societies discouraging men from expressing vulnerability or seeking psychological support.
3. Social Support and Community Health
- Family and Peer Influence- Social networks play a vital role in shaping health behaviors and providing emotional support during illness (Murphy & Bennett, 2004).
- Public Health Interventions- Community-based programs focusing on preventive care, mental health awareness, and social inclusion have been shown to improve population health outcomes (Sallis et al., 2006).
Implications for Public Health and Policy
To promote equitable health outcomes, policies must address gender disparities, lifespan-specific health needs, and socio-cultural influences.
- Gender-Sensitive Healthcare Policies- Ensuring that medical research, diagnostics, and treatments account for gender differences in disease presentation and response.
- Lifespan-Specific Health Interventions- Developing age-appropriate health initiatives, from childhood nutrition programs to elderly healthcare support systems.
- Addressing Socioeconomic Disparities- Expanding access to affordable healthcare, improving health literacy, and reducing economic barriers to medical services.
- Integrating Cultural Competency in Healthcare- Training healthcare professionals to understand and respect diverse cultural beliefs and practices in medical decision-making.
Conclusion
The biopsychosocial model highlights the interconnectedness of gender, lifespan development, and socio-cultural factors in shaping health outcomes. By recognizing these influences, healthcare systems can develop more inclusive, effective, and equitable health strategies that address the diverse needs of individuals across different life stages and cultural contexts.
References
Braveman, P., Egerter, S., & Williams, D. R. (2011). The social determinants of health: Coming of age. Annual Review of Public Health, 32, 381-398.
Courtenay, W. H. (2000). Constructions of masculinity and their influence on men’s well-being: A theory of gender and health. Social Science & Medicine, 50(10), 1385-1401.
La Greca, A. M., & Stone, W. L. (1985). Peer influence on risk-taking behavior in adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 14(6), 401-409.
Marmot, M. (2005). Social determinants of health inequalities. The Lancet, 365(9464), 1099-1104.
Sarafino, E. P., & Smith, T. W. (2020). Health psychology: Biopsychosocial interactions (10th ed.). Wiley.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 18,526 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, February 12). Influence of 3 Important Factors on Health: Gender, Life-Span Development, and Socio-Cultural Factors. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/influence-of-3-important-factors-on-health/
