Introduction to Factors Affecting Personality
Personality, as defined by the American Psychological Association (APA), refers to the “individual differences in characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving” (APA, 2021). Gordon Allport, a prominent figure in personality psychology, offered another foundational definition. He described personality as “the dynamic organization within the individual of those psychophysical systems that determine his unique adjustments to his environment” (Allport, 1937). Allport emphasized that personality is an active and evolving system that encompasses both mental and physical aspects, which together guide an individual’s behaviours and interactions with their environment.
Personality is influenced by a wide range of factors throughout life. Genetics, family dynamics, culture, education, trauma, peer influence, biological factors, and even media exposure all contribute to the formation and evolution of personality traits. Understanding these influences allows for a deeper appreciation of the complexity and uniqueness seen across individuals.
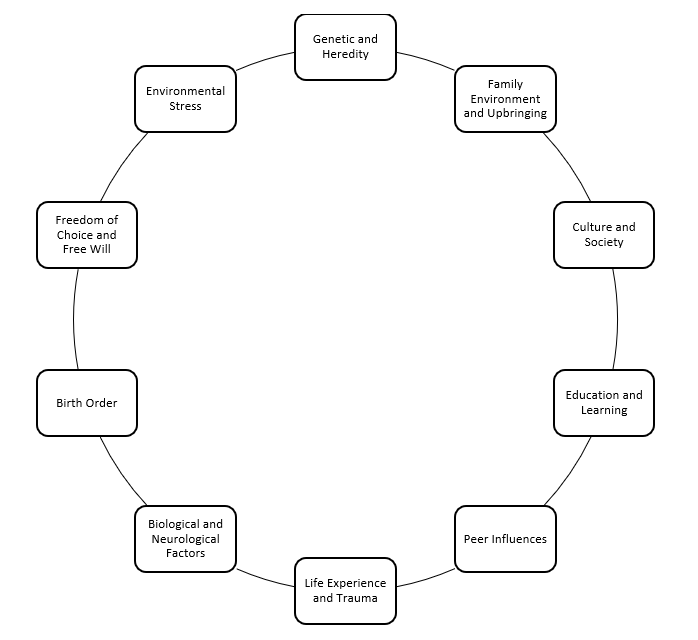
Factors Affecting Personality
Factors Affecting Personality
1.Genetics and Heredity
Intrinsic Factor.
The role of genetics in personality development is significant, as it lays the foundation for many personality traits. Numerous studies have explored the genetic basis of personality traits such as extraversion, neuroticism, and openness to experience, suggesting that heredity accounts for a substantial portion of individual differences in personality. Bouchard (2004) emphasized that twin studies have shown a strong genetic component to personality, with identical twins often displaying more similar personality traits than fraternal twins or siblings raised together. Genetic predispositions influence the potential for certain personality traits, but environmental factors modify and shape these tendencies over time.
The interaction between genes and the environment is crucial in understanding personality development. While some genetic traits are inherited, their expression can be significantly influenced by life experiences and the surrounding environment. Genetic studies in psychology have illuminated the interplay between nature and nurture, providing a framework for understanding how intrinsic factors contribute to individual personality differences.
- Family Environment and Upbringing
Extrinsic Factor.
The family environment plays an equally important role in shaping personality. From early childhood, family dynamics and parental interactions form the bedrock of personality development. According to Bowlby’s attachment theory (1969), early relationships with primary caregivers significantly influence emotional development and attachment styles. A secure attachment in childhood fosters positive personality traits such as confidence and resilience, while insecure attachment may lead to anxiety, dependence, or avoidance in later life.
Parenting styles, ranging from authoritative to permissive, also Mold the personality of the child. An authoritative parenting style, which combines warmth with clear boundaries, is often associated with well-adjusted and confident personalities. In contrast, neglectful or authoritarian parenting may lead to the development of maladaptive traits, such as aggression or low self-esteem. The impact of family environment on personality development is profound and can be seen throughout an individual’s life, shaping their worldview and interpersonal relationships.
- Culture and Society
Culture provides the external framework in which personality is expressed and developed. Cross-cultural psychology has shown that cultural norms, values, and societal expectations significantly shape personality (Triandis & Suh, 2002). For example, collectivist cultures, which emphasize group harmony and interdependence, may foster personality traits such as cooperation, humility, and a strong sense of community. In Japan, for instance, individuals often prioritize group consensus and avoid open conflict to maintain social harmony. Conversely, individualistic cultures, which emphasize personal achievement and autonomy, may promote traits such as assertiveness, self-reliance, and competitiveness. In the United States, a highly individualistic society, success is often measured by personal accomplishments, with traits like assertiveness and independence being highly valued.
Lev Vygotsky’s theory further supports the idea that culture affects personality development. According to Vygotsky, cognitive development is deeply rooted in social interaction and the transmission of cultural knowledge. For example, in cultures where respect for elders is paramount, such as in many Indigenous communities, children learn to develop deference and humility early on through interaction with older generations. Similarly, in Western cultures where individual rights and self-expression are emphasized, children are often encouraged to think critically and assert their own opinions. Cultural values, transmitted through language, education, and social interactions, influence not only what individuals think but also how they think and behave within a societal context, shaping their personalities in accordance with cultural expectations.
- Education and Learning
The educational system and learning experiences profoundly influence cognitive and social development, which in turn affect personality traits. Schools are social institutions where individuals interact with peers and authority figures, fostering the development of social skills, self-discipline, and resilience. Educational psychology examines how these interactions shape not just intellectual growth but also emotional and personality development (Ormrod, 2011).
Formal education teaches problem-solving, critical thinking, and adaptability—skills that are closely tied to personality traits such as openness and conscientiousness. Furthermore, teachers and mentors can serve as role models, providing guidance that shapes values, self-concept, and overall personality. Learning experiences, both in structured educational settings and in everyday life, contribute to the ongoing development and refinement of personality traits.
- Peer Influence
Extrinsic Factor.
Peer influence is especially pronounced during adolescence, a critical period for personality development. As adolescents seek acceptance and social belonging, peer groups can significantly shape their attitudes, behaviours, and personality traits. The desire to fit in with peers may lead to the adoption of certain behaviours and values, a phenomenon well-documented in social psychology (Asch, 1955). Peer pressure can encourage conformity, risk-taking, or rebellion, depending on the dynamics of the group.
While peer influence can have both positive and negative effects, it is an undeniable factor in shaping social behaviours and personality development. Individuals learn about social roles, communication, and cooperation within their peer groups, all of which contribute to their evolving personality.
- Life Experiences and Trauma
Life events, particularly those involving trauma, can have lasting effects on personality. Trauma, such as abuse, loss, or violence, can fundamentally alter how an individual interacts with the world and others. Van der Kolk et al. (1996) examined the profound impact of trauma on personality development, highlighting how trauma can lead to dissociation, emotional dysregulation, and the development of specific coping mechanisms. Traumatic experiences can contribute to the emergence of disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or result in more resilient personality traits, depending on the individual’s support system and coping strategies.

The Body Keeps the Score
Significant life events, such as marriage, career changes, or the death of a loved one, also shape personality by forcing individuals to adapt to new circumstances. Positive experiences can foster traits like optimism and perseverance, while negative experiences can lead to anxiety or neuroticism.
- Biological and Neurological Factors
Personality is closely linked to biological and neurological factors. Research in neuroscience has identified the brain structures and neurotransmitters that influence personality traits. For example, DeYoung (2015) explored how the dopaminergic system relates to openness and exploration, while the serotonin system is linked to emotional stability and conscientiousness. Brain injuries, neurodegenerative diseases, and hormonal imbalances can also lead to significant changes in personality, demonstrating the importance of neurological health in maintaining personality stability.
Additionally, variations in brain structure have been associated with different personality traits. For example, studies have shown that individuals with larger prefrontal cortices tend to exhibit higher levels of self-control and conscientiousness. This growing body of research highlights the biological underpinnings of personality and how neurological processes contribute to individual differences.
- Environmental Stressors
Environmental stressors such as poverty, discrimination, and chronic stress can significantly impact personality development. Health psychology has shown that prolonged exposure to stress can lead to the development of anxiety, depression, and maladaptive personality traits (Cohen et al., 2007). Chronic stress affects both mental and physical health, which can, in turn, influence personality traits such as neuroticism and pessimism.
For individuals living in high-stress environments, adaptive coping mechanisms may develop, leading to traits like resilience and perseverance. However, chronic stress without adequate support can lead to the development of negative personality traits and mental health disorders, illustrating the importance of environmental conditions in shaping personality.
- Birth Order
Birth order has long been considered a factor in personality development, although its influence remains a topic of debate. Some theories suggest that firstborn children may develop leadership qualities and a sense of responsibility, while middle children may become more adaptable and diplomatic, and youngest children may exhibit rebellious or attention-seeking behaviors. While these patterns are not universally applicable, birth order can influence personality by shaping the dynamics of sibling relationships and parental expectations.
Alfred Adler, a prominent psychologist, expanded on this idea, suggesting that firstborns often feel a sense of dethronement when siblings arrive, which may lead to a greater need for achievement. Middle children, he believed, may feel overlooked, driving them to become peacemakers or highly competitive, while youngest children might develop a need for attention or display more carefree traits due to the indulgence they receive from family. These dynamics, Adler argued, contribute to the development of distinct personality traits within each birth order position.
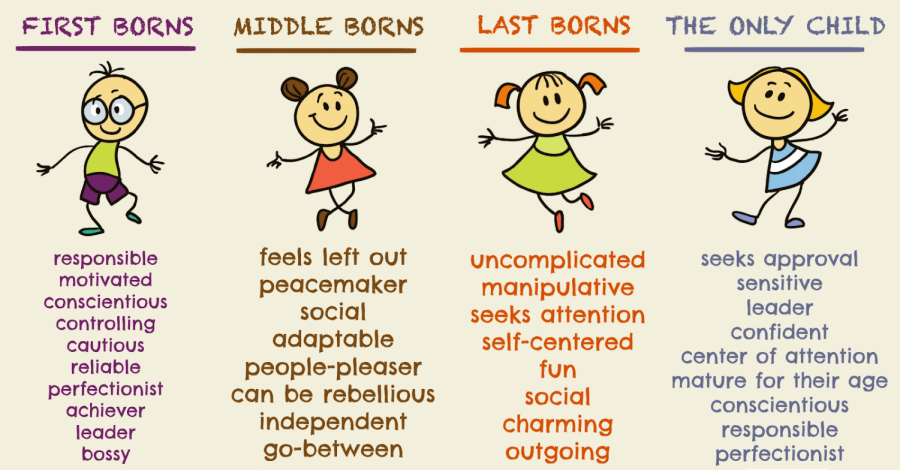
Birth Order (Medium)
- Personal Choices and Free Will
Intrinsic Factor.
Personal agency and the choices individuals make throughout their lives play a critical role in shaping personality. Positive psychology emphasizes the importance of personal values, goals, and the pursuit of self-improvement in personality development (Seligman, 2002). Individuals who take active control over their lives, setting goals and striving for personal growth, are more likely to develop traits such as optimism, resilience, and conscientiousness.
The exercise of free will allows individuals to break free from limiting circumstances or negative influences, leading to the development of a more authentic and self-determined personality. Personal choices, in combination with external factors, continuously shape personality throughout life.
- Media and Technology
In the digital age, media and technology have become powerful forces in shaping personality. The consumption of media—whether through television, social media, or the internet—can influence individuals’ values, beliefs, and behaviours. For example, exposure to certain media content can reinforce stereotypes, shape attitudes, and even affect self-esteem. Social media platforms, in particular, have been shown to impact personality traits such as self-consciousness and narcissism, as individuals curate their online personas to align with social expectations.
Furthermore, the constant influx of information and media stimuli can affect cognitive processes and emotional regulation, highlighting the role of media in the development and expression of personality traits.
- Biological Aging and Developmental Stages
Personality is not static but evolves over time as individuals pass through different developmental stages. Maturation, hormonal changes, and life transitions contribute to personality shifts. Research suggests that certain traits, such as conscientiousness and emotional stability, tend to increase with age, while traits such as openness may decline (Roberts & Mroczek, 2008). Biological aging and life experiences contribute to the natural progression of personality traits, with older individuals often displaying greater emotional regulation and wisdom.
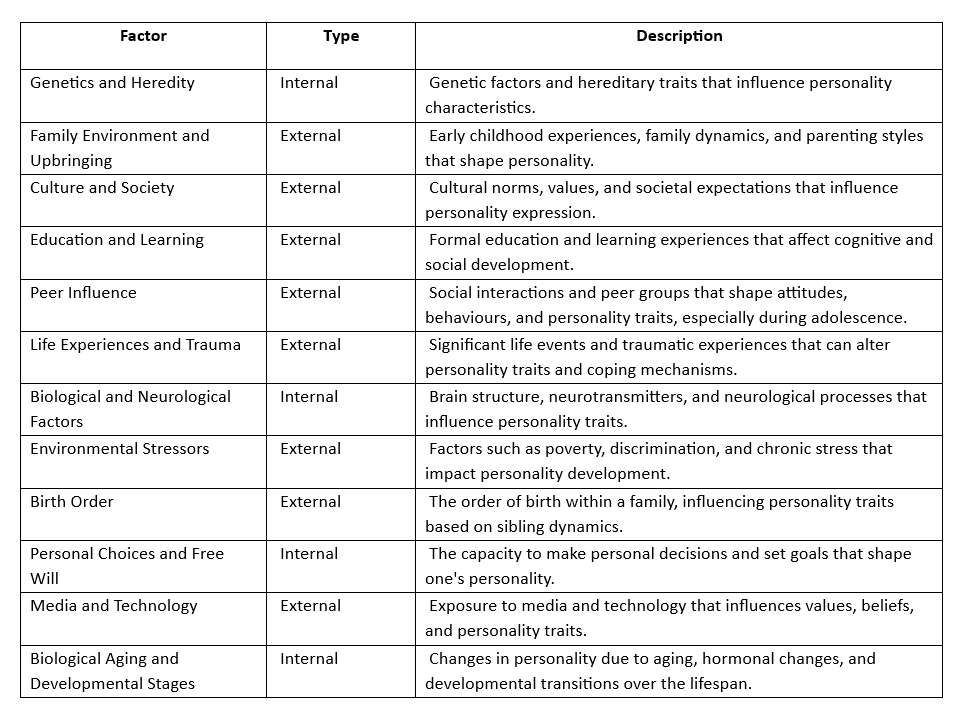
Factors Affecting Personality
Conclusion and Implication
Personality development is a multifaceted process, and understanding its intricacies has significant implications across various domains of life, including mental health, education, career development, and interpersonal relationships. The dynamic interplay of genetic, environmental, biological, and experiential factors highlights how personality evolves over time, with profound effects on an individual’s overall functioning and well-being.
In conclusion, the study of personality development has far-reaching implications for various aspects of life. From improving mental health treatment to enhancing educational strategies, career development, relationships, and personal growth, understanding the complex factors that shape personality can lead to more effective interventions, better outcomes, and a deeper appreciation of individual uniqueness.
References
Allport, G. W. (1937). Personality: A psychological interpretation. Holt.
American Psychological Association. (2021). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association.
Asch, S. E. (1955). Opinions and social pressure. Scientific American, 193(5), 31-35. https://doi.org/10.1038/scientificamerican1155-31
Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment and loss: Volume I. Attachment. Basic Books.
Bouchard, T. J. (2004). Genetic influence on human behaviours. In D. M. Buss (Ed.), The handbook of evolutionary psychology (pp. 112-131). Wiley.
Cohen, S., Janicki-Deverts, D., & Miller, G. E. (2007). Psychological stress and disease. JAMA, 298(14), 1685-1687. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.14.1685
DeYoung, C. G. (2015). The personality neuroscience of openness to experience. In M. R. Leary & J. P. Tangney (Eds.), Handbook of self and identity (2nd ed., pp. 462-483). Guilford Press.
Ormrod, J. E. (2011). Educational psychology: Developing learners (7th ed.). Pearson.
Roberts, B. W., & Mroczek, D. K. (2008). Personality trait change in adulthood. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 17(1), 31-35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8721.2008.00543.x
Seligman, M. E. P. (2002). Authentic happiness: Using the new positive psychology to realize your potential for lasting fulfilment. Free Press.
Triandis, H. C., & Suh, E. M. (2002). Cultural influences on personality. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 133-160. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135200
Van der Kolk, B. A., McFarlane, A. C., & Weisaeth, L. (1996). Trauma and its wake: The study and treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. Guilford Press.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Harvard University Press.
Subscribe to Careershodh
Get the latest updates and insights.
Join 18,509 other subscribers!
Niwlikar, B. A. (2023, October 10). Factors Affecting Personality- Discover the 10 Insightful Influences to Personality Development. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/factors-affecting-personality/

Your comprehensive breakdown of the factors influencing personality sheds light on the dynamic nature of human development. It’s insightful to see how external and internal factors intertwine to shape our personalities.
Thank You!