Introduction
Communication is central to human interaction and emotional expression. The way individuals communicate their thoughts and feelings greatly influences relationships, self-understanding, and psychological well-being. In counselling psychology, communication is viewed not only as a means of exchanging information but also as a vehicle for expressing emotions, needs, and personal meanings. Creating it involves awareness and regulation of feelings along with the use of verbal, vocal, and bodily channels of expression.
Nelson-Jones (2000) emphasizes that it are learnable and can be enhanced through counselling. Effective communication enables individuals to express feelings constructively, understand others accurately, and manage interpersonal relationships more effectively.
Read More: Mind Skills
Communication and Feelings
Feelings are internal emotional experiences that influence thoughts, behavior, and communication. Often, individuals struggle not because of emotions themselves, but because they lack effective ways to communicate those emotions. According to Gladding (2014), unexpressed or poorly expressed feelings can lead to misunderstanding, conflict, and psychological distress.
Verbal Communication
Counselling helps individuals become aware of their emotions and learn appropriate ways to express them. Emotional awareness and communication are closely linked; recognizing feelings is the first step toward expressing them in healthy ways (Nelson-Jones, 2000). Developmental research shows that emotional expression skills evolve over time and are shaped by family, culture, and social learning (Berk, 2003).
1. Verbal Communication
Verbal communication refers to the use of spoken or written words to convey messages. In counselling, it includes the choice of words, clarity of expression, and the ability to articulate thoughts and feelings accurately. Effective verbal communication helps individuals name emotions, describe experiences, and communicate needs (Gibson & Mitchell, 2003).
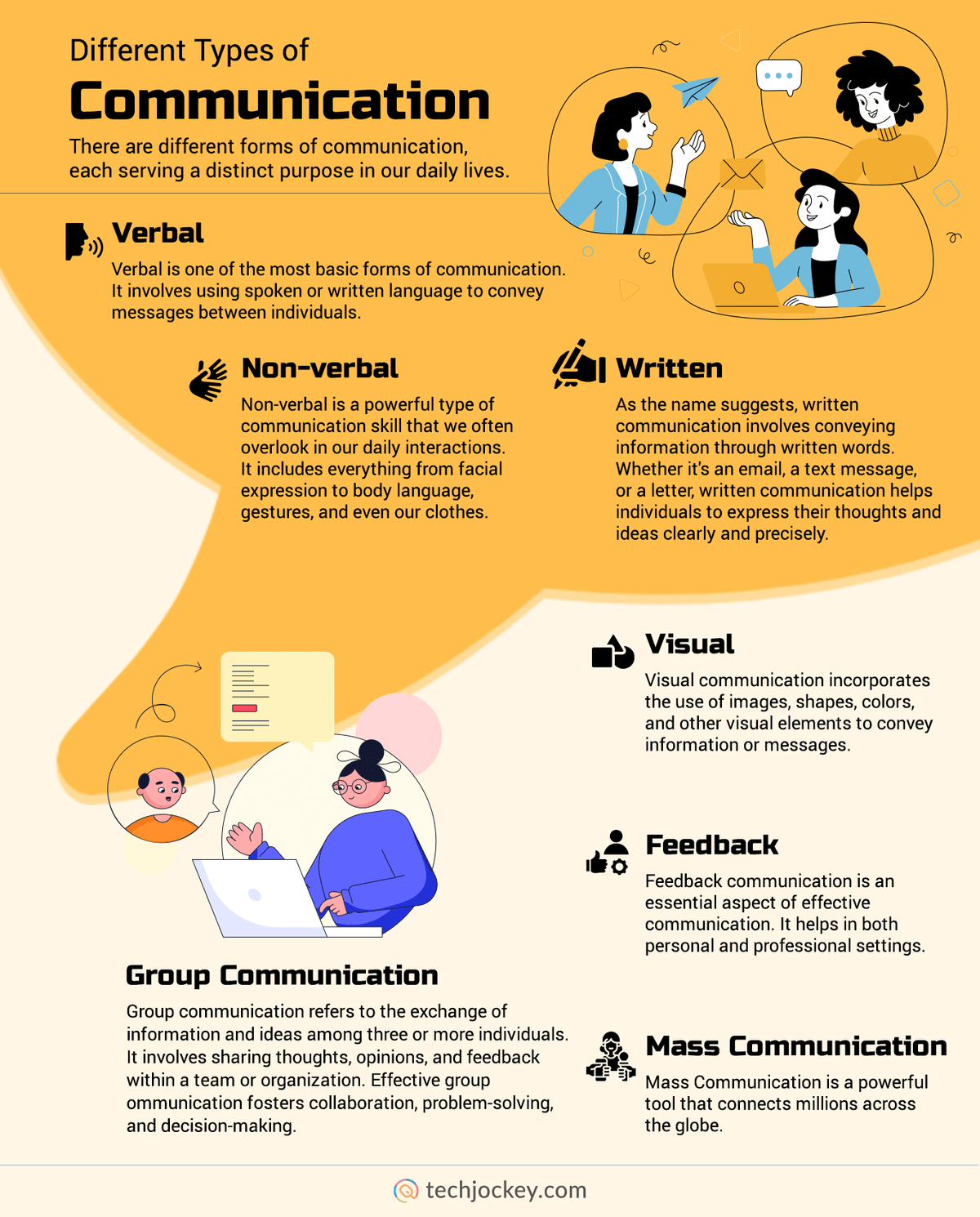
7 Types of Communication
In counselling settings, clients are encouraged to use “I-statements” to express feelings without blaming others, such as “I feel anxious when…” rather than accusatory language. Clear verbal expression reduces misunderstandings and promotes assertive communication. For children and adolescents, vocabulary development plays a key role in emotional expression (Berk, 2003).
2. Vocal Communication
Vocal communication refers to how something is said rather than what is said. It includes tone, pitch, volume, speed, and pauses in speech. Vocal cues often convey emotions more powerfully than words alone. For example, hesitation may signal anxiety, while a raised voice may indicate anger or frustration (Nelson-Jones, 2000).
Counsellors attend closely to it to understand clients’ emotional states. Inconsistencies between verbal content and vocal tone may indicate unexpressed or conflicting feelings. Learning to regulate vocal expression helps individuals communicate emotions more effectively and reduces interpersonal conflict (Capuzzi & Gross, 2008).
3. Bodily (Non-Verbal) Communication
Bodily communication, also known as non-verbal communication, includes facial expressions, gestures, posture, eye contact, and body movements. Research suggests that a large portion of emotional communication occurs non-verbally. Non-verbal cues often reflect genuine feelings that may not be verbally expressed (Gelso & Fretz, 1995).

Non-Verbal Communication
In counselling, bodily communication is important for both the counsellor and the client. Open posture, appropriate eye contact, and relaxed body movements convey acceptance and empathy. For clients, becoming aware of bodily signals helps them understand and regulate emotional reactions. Children, in particular, rely heavily on bodily communication to express feelings (Kapur, 2011).
Integration of Communication Channels
Effective communication involves congruence between verbal, vocal, and bodily channels. When words, tone, and body language align, it becomes clear and authentic. Incongruence, such as saying “I’m fine” with a tense posture and flat tone, may signal suppressed emotions (Nelson-Jones, 2000).
Counselling helps individuals recognize inconsistencies in it and practice more integrated expression. Group counselling provides additional opportunities to observe and improve communication patterns through feedback and role-play (Corey, 2008).
Developmental Considerations
Communication and emotional expression develop progressively across the lifespan. Young children rely heavily on non-verbal and behavioral expression, while adolescents and adults develop more complex verbal and emotional communication skills (Papalia, Olds, & Feldman, 2004). Counselling interventions must be tailored to the client’s developmental level to be effective.
Conclusion
Creating effective communication involves developing awareness of feelings and learning to express them through verbal, vocal, and bodily channels. Healthy communication promotes emotional regulation, interpersonal understanding, and psychological well-being. Counselling plays a vital role in helping individuals recognize emotions, improve communication skills, and achieve congruence between thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
References
Berk, L. E. (2003). Child development (6th ed.). Delhi: Prentice Hall of India.
Capuzzi, D., & Gross, D. R. (2008). Counseling and psychotherapy: Theories and interventions (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
Corey, G. (2008). Theory and practice of group counseling. Thomson Brooks/Cole.
Gelso, C. J., & Fretz, B. R. (1995). Counselling psychology. Bangalore: Prism Books Pvt. Ltd.
Gibson, R. L., & Mitchell, M. H. (2003). Introduction to counselling and guidance (6th ed.). Pearson Education.
Gladding, S. T. (2014). Counselling: A comprehensive profession (7th ed.). Pearson Education.
Kapur, M. (2011). Counselling children with psychological problems. Dorling Kindersley.
Nelson-Jones, R. (2000). Introduction to counselling skills. Sage Publications.
Papalia, D. E., Olds, S. W., & Feldman, R. D. (2004). Human development (9th ed.). Tata McGraw-Hill.
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, December 18). Creating Your Communication and Feelings With 3 Important Communications. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/communication-and-feelings/
