Introduction
Opioid-Related and Sedative-Hypnotic/Anxiolytic-Related Disorders are among the most serious substance-use conditions due to their high potential for dependency, overdose, and withdrawal complications. Opioids (e.g., heroin, morphine, prescription painkillers) and sedative-hypnotics (e.g., benzodiazepines, barbiturates) act on the nervous system to reduce pain, induce relaxation, or decrease anxiety. Prolonged use disrupts the brain’s reward pathways, leading to tolerance, cravings, dependence, psychological disturbance, and severe health risks.
Read More: Cluster C Disorder
1. Opioid-Related Disorders
Opioid-Related Disorders involve dependence on or misuse of opioids such as heroin, morphine, oxycodone, or fentanyl. These substances produce intense euphoria and pain relief but also create strong physical dependence, tolerance, and dangerous withdrawal symptoms—making them highly addictive and prone to overdose.
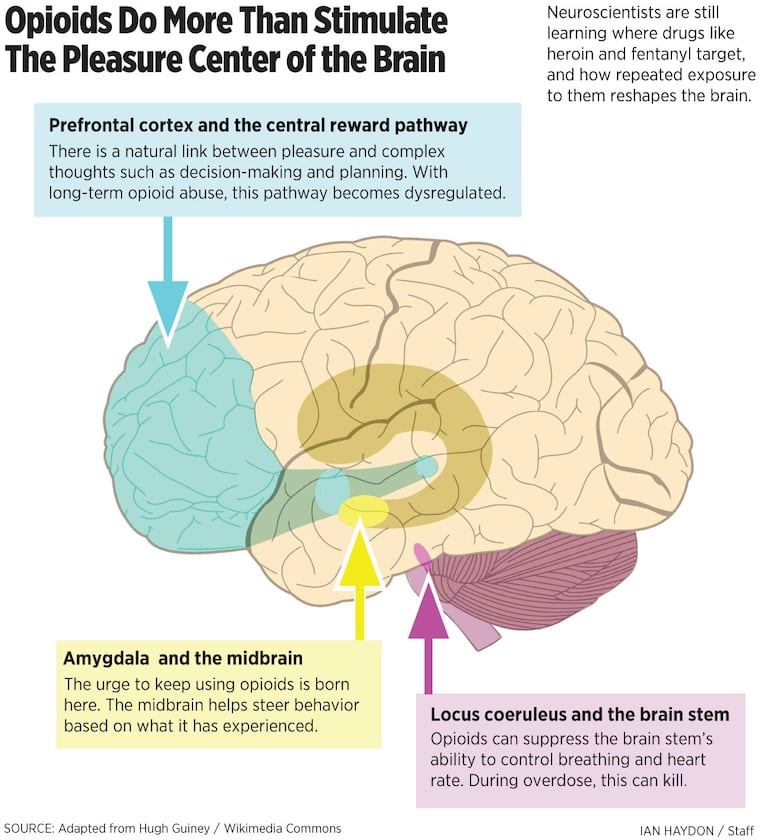
Opioid-Related Disorders
Diagnostic Features (DSM-5)
Some features include:
- Intense Euphoria Followed by Dysphoria – pleasurable “high” followed by sedation.
- Tolerance and Withdrawal – strong physiological dependence; painful withdrawal symptoms.
- Craving – compulsive urge to seek opioids.
- Impaired Control – difficulty cutting down or regulating use.
- Social/Occupational Dysfunction – neglect of roles, isolation, financial loss.
- Risky Use – using in dangerous situations or despite medical complications.
- Overdose Potential – respiratory depression leading to coma or death.
Types of Opioids
Some types of opioids include:
- Natural Opioids: Morphine, codeine.
- Semi-Synthetic Opioids: Heroin, oxycodone, hydrocodone.
- Synthetic Opioids: Fentanyl, methadone, tramadol.
Causes and Risk Factors
Some causes include:
1. Biological Factors
- Genetic predisposition to addiction.
- Dopamine reward system sensitivity.
- Chronic pain conditions.
2. Psychological Factors
- Depression, anxiety, trauma, emotional dysregulation.
- Use as self-medication.
3. Social Factors
- Over-prescription of painkillers.
- Peer influence and high availability.
- Poverty, homelessness, stress.
Treatment Approaches
Some treatment approaches include:
1. Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
- Methadone: long-acting opioid preventing withdrawal.
- Buprenorphine: partial opioid agonist reducing cravings.
- Naltrexone: opioid antagonist preventing euphoric effects.
2. Psychotherapy
- CBT, Motivational Interviewing, relapse prevention.
- Trauma-focused therapies for underlying emotional distress.
3. Harm Reduction
- Naloxone for overdose reversal.
- Needle exchange programs.
- Safe consumption facilities.
Naloxone
2. Sedative-Hypnotic or Anxiolytic-Related Disorders
These disorders involve misuse of substances like benzodiazepines, barbiturates, or sleep medications that depress the central nervous system. While often prescribed for anxiety or insomnia, long-term use can lead to tolerance, dependence, cognitive impairment, and life-threatening withdrawal reactions.
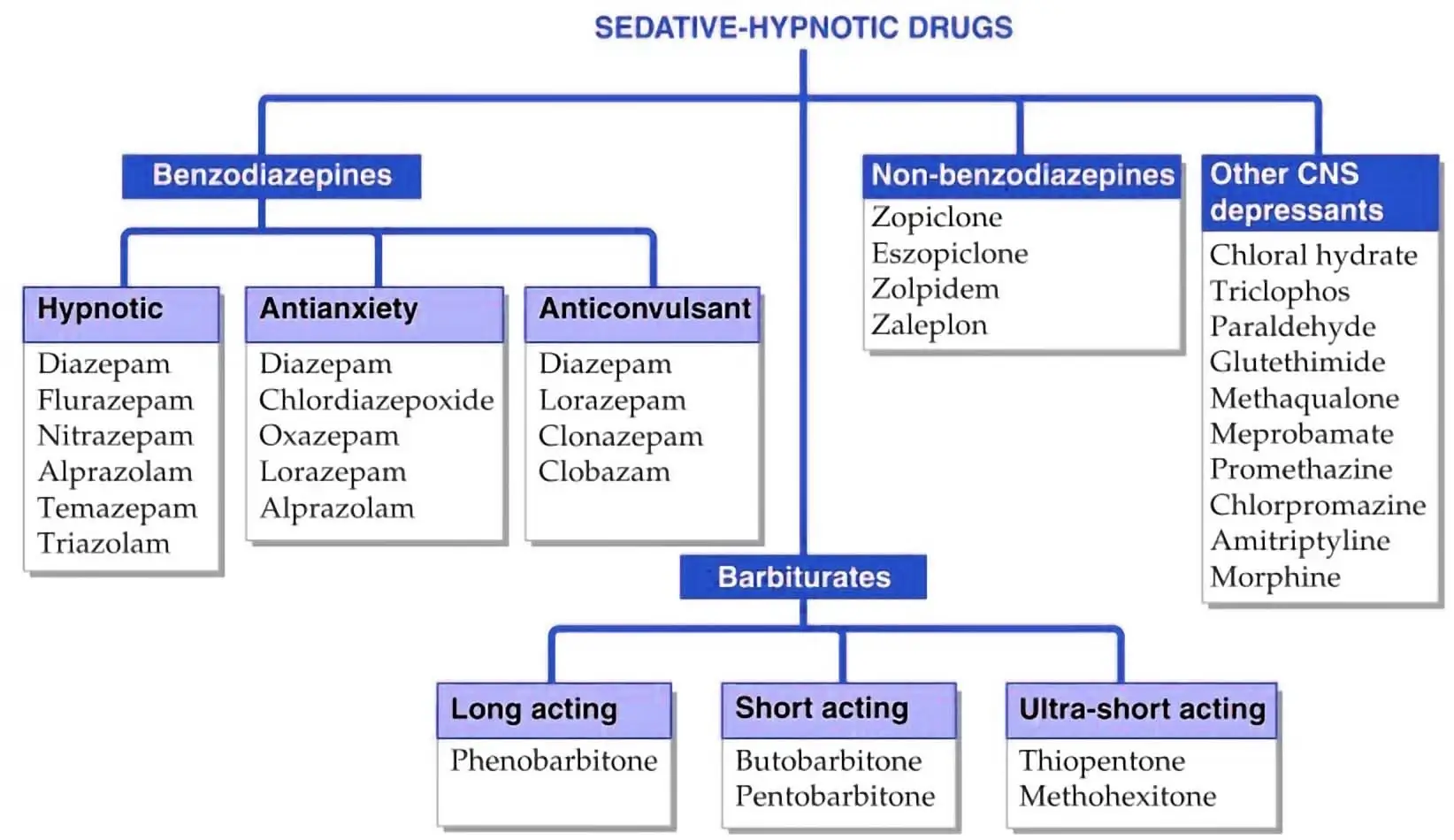
Sedative-Hypnotic Disorders
Diagnostic Features (DSM-5)
Some features include:
- CNS Depression – slowed thinking, drowsiness, impaired coordination.
- Cognitive Impairment – memory problems and confusion.
- Tolerance and Dependence – need for increasing doses.
- Severe Withdrawal – seizures, insomnia, agitation (can be life-threatening).
- Loss of Control – inability to reduce or regulate use.
- Behavioral Changes – irritability, emotional instability.
- Functional Impairment – occupational, academic, or interpersonal difficulties.
Types
Some types include:
- Benzodiazepines: Diazepam, lorazepam, alprazolam.
- Barbiturates: Phenobarbital, pentobarbital.
- Z-Drugs: Zolpidem, eszopiclone (used for sleep).
Causes and Risk Factors
Some causes include:
1. Biological Factors
- Genetic vulnerability to anxiety or substance dependence.
- Brain dependence due to long-term prescription use.
2. Psychological Factors
- Anxiety disorders, panic attacks, insomnia.
- Stress management deficits.
3. Social Factors
- Medical prescriptions leading to long-term use.
- Easy access through healthcare providers.
- Stressful life environment.
Treatment Approaches
Some treatment approaches include:
1. Medication
- Gradual tapering of benzodiazepines.
- Anticonvulsants for withdrawal.
- Antidepressants (SSRIs) for anxiety disorders.
2. Psychotherapy
- CBT for anxiety and insomnia.
- Mindfulness-based stress reduction.
- Behavioral sleep therapy.
3. Rehabilitation
- Inpatient detox for severe dependence.
- Long-term relapse prevention programs.
Conclusion
Opioid and sedative-hypnotic disorders pose significant public health challenges due to their addictive potential and life-threatening consequences. Effective treatment requires integrated care, combining medication-assisted therapy, psychological interventions, and preventive strategies. Early identification, supportive counseling, and careful medical management are essential in promoting long-term recovery.
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.).
Butcher, J. N., Hooley, J. M., & Mineka, S. (2014). Abnormal Psychology (15th ed.).
Carson, R. C., Butcher, J. N., & Mineka, S. (2007). Abnormal Psychology (13th ed.).
Nevid, J. S., Rathus, S. A., & Greene, B. (2014). Abnormal Psychology (9th ed.).
Sue, D., Sue, D. W., & Sue, S. (2006). Understanding Abnormal Behavior (8th ed.).
Niwlikar, B. A. (2025, December 11). Opioid-Related & Sedative-Hypnotic/Anxiolytic-Related Disorders: Features, Causes, and 3 Important Treatment. Careershodh. https://www.careershodh.com/opioid-sedative-hypnotic-anxiolytic/
